Receptacle Grades:
What Do They Mean?
By Chuck Kurten, Principal
Engineer (PDE) for Wiring Devices & Components, Underwriters
Laboratories Inc.
As a receptacle is being
chosen or approved for an application, one should first
identify the appropriate grade and features that conform to
the safety standards, codes, and suitability.
In today’s world there are
so many different types of receptacles to choose from —
straight blade, locking-type, and pin and sleeve. The
variety of straight blade receptacles offered by
manufacturers alone is staggering — in fact, wiring device
manufacturers produce and market more than a 1,000 different
types. Differences include electrical rating, color, style,
sizes, and configuration. Receptacles are marketed using
terms such as general grade, specification grade, heavy
duty, industrial grade, commercial grade, residential grade,
hospital grade, specialty grade, and fed spec. There are,
however, only four receptacle identities are being specified
in the Standard for Attachment Plugs and Receptacles,
ANSI/UL 498 and CSA CAN/C22.2 No. 42-99, General Use
Receptacles, Attachment Plugs, and Similar Wiring Devices.
Grade Designations, Marketing Information and Product Features
In these standards,
straight blade receptacles are assigned four grades: general
use, hospital, federal specifications (fed. spec.), and
combination hospital/fed. spec. Each grade has its own
distinct marking requirements. The standards do not
acknowledge the other receptacle marketing designations
(e.g., commercial grade or heavy duty).
These designations
represent the manufacturer’s attempt to assist in the
selection process of an appropriate straight blade
receptacle based upon the intended usage and demands that
may be placed on the device. While they may be helpful to
the user, these designations generally have no impact on the
safety requirements applicable to the receptacles.
Marketing designations are
different from design features. Manufacturers also offer
straight blade receptacles with a variety of special
features. These features may include resistance to
environmental conditions, tamper resistant construction, or
isolated ground. For example, an isolated ground straight
blade receptacle is offered in all the different grades —
General Use, Hospital, Fed. Spec. and combination
Hospital/Fed. Spec.
The standards require
additional investigation to address compliance of these
special receptacle features.
General Use Receptacles
General use receptacles are
the most common found in the marketplace in both the United
States and Canada. General use receptacles are intended to
supply a variety of electrical loads in general use, and are
tested for this variety. For general use receptacles,
matching the plug configuration with the receptacle
configuration is the key step in determining if the
receptacle can handle the load. In this case, the receptacle
has been evaluated to ensure it can handle the load whether
it is a lamp, vacuum cleaner, heater, or other product.
(See Figure 1)
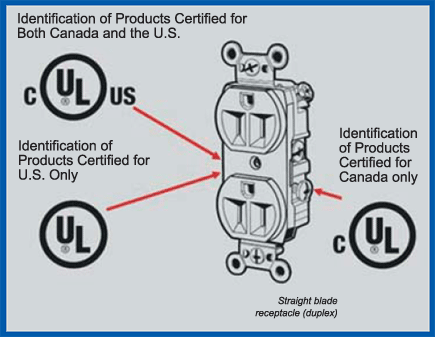
Figure 1. Identification of product certified for both
Canada and the U.S. - general use
Hospital
Grade Receptacles
In addition to complying
with the general use requirements, hospital grade
receptacles are specially designed and are subject to
additional requirements of the standards. These include
additional grounding reliability, assembly integrity,
strength and durability.
Hospital grade receptacles
are offered in 15 A and 20 A straight blade of the ANSI/NEMA
WD6 5-15, 6-15, 5-20 and 6-20 configurations. They are
intended for use in accordance with the National Electrical
Code, ANSI/NFPA 70, Article 517 (Health Care Facilities) in
the United States and the Canadian Electrical Code, Part 1
CAN/C22.1.02, Section 24 (Patient Care Areas) in Canada.
Hospital grade receptacles
have the same markings appearing on general use receptacles,
but include additional markings denoting their intended use.
These additional markings include the phrase “Hospital
Grade” or ”Hosp. Grade” appearing on the back of the
receptacle (where visible during installation) and a green
dot located on the face, visible after installation with a
cover plate secured as intended. UL does offer listing to a
special locking-type receptacle rated 20 A, 125 V. The
identification is very similar except it is marked ”Hospital
only" with no green dot appearing on the face. (See
Figure 2)
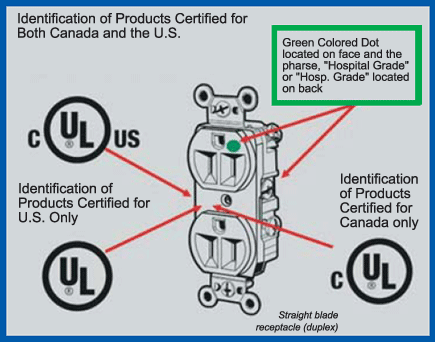
Figure 2. Identification of product certified for both
Canada and the U.S. - hospital grade
Federal
Specification General Use Receptacles
In addition to complying
with the general use requirements, fed. spec. receptacles
have also been investigated for compliance with US Federal
Specification W-C-596, "General Specification for Electrical
Power Connectors." The Federal Specification W-C-596 is a
document produced by the General Service Administration of
the U.S. Federal Government. It identifies
constructionfeatures, marking specifications and performance
requirements beyond the requirements of the safety
standards, for the purpose of durability and service life.
Underwriters Laboratories is authorized to apply the federal
specification verification mark.
The fed. spec. was created
as a means to help government procurement personnel in
obtaining the correct receptacle from suppliers. The fed.
spec. details configuration, electrical rating, type (single
outlet or duplex) and even including the color of the outlet
face, assigning a common descriptor. The receptacle industry
adheres to this identification scheme in lieu of their usual
catalog designations to facilitate government purchases.
Receptacles are identified
by the federal specification verification mark, capital
letters “F" and “S“ each in a wing on either side of the UL
Listing Mark. The manufacturer may also indicate the federal
specification number “W-C-596F“ or “W-C-596G“ with the
federal specification part number which consists of the
appropriate specification sheet and dash number described in
the specification. These may appear on the device or on the
smallest container in which the device is packaged.
Other wiring devices
eligible for fed. spec. rating include attachment plugs,
cord connectors, (cable outlets) receptacles and male
inlets. They are offered in both straight blade and
locking-type configurations and an electrical rating ranging
from 120 to 600 volts with current ratings up to 60 amperes
and a frequency rating of 50/60 hertz. (See Figure 3)
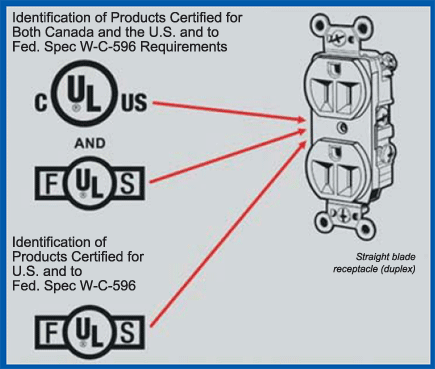
Figure 3. Identification of product certified for both
Canada and the U.S. and to Fed. Spec. W-C-596 requirements
Hospital
Grade/Fed. Spec. Receptacles
As the grade name
indicates, hospital grade/fed. spec. receptacles have been
investigated for compliance with fed. spec. hospital grade
requirements. They too are identified by the capital letters
“F“ and “S“ flanking the UL Listing Mark. The manufacturer
may also indicate the additional federal specification
information on the device or on the smallest container in
which the device is packaged. The phrase “Hospital Grade“ or
“Hosp. Grade“ will appear on the back of the receptacle
(where visible during installation) and a green dot will be
present on the face, visible after installation with a cover
plate secured as intended.
From time to time UL is
asked the question — “What’s the difference between a fed.
spec. and a combination hospital grade/fed. spec receptacle
besides the addition of the green dot and hospital grade
identifier?”
Although they seem to
visually appear the same, they are not. Each is investigated
to a different set of performance and construction
requirements. For example, a fed. spec. receptacle is not
subject to the abrupt plug removal performance sequence of
testing, whereas a hospital grade/fed. spec. is subject to
this performance test sequence.
So, as a receptacle is
being chosen or approved for an application, the decision
making process should begin by identifying the appropriate
grade (e.g., general use) and features (e.g., tamper
resistant) that conform to the safety standards and codes,
and suit the particular installation. This information is
different than the manufacturer’s designations (e.g., heavy
duty) intended to meet the user’s preferences for the
application. (See Figure 4)
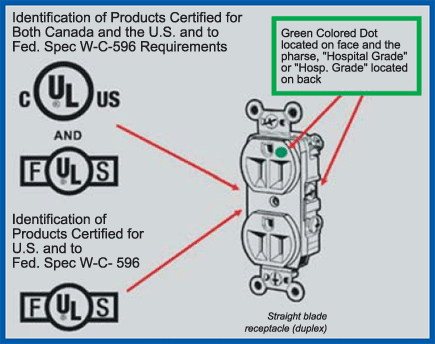
Figure 4. Identification of product certified for both
Canada and the U.S. and to Fed. Spec. W-C-596 - hospital
grade/ feb. spec. receptacles
By Chuck Kurten, Principal Engineer (PDE) for Wiring
Devices & Components, Underwriters Laboratories Inc. |